07 Import Bitcoin into Tigergraph
bitcoin-to-neo4j: https://github.com/in3rsha/bitcoin-to-neo4j/blob/master/docs/how.md bitcoin-to-tigergraph: https://github.com/tigergraph/bitcoin-to-tigergraph
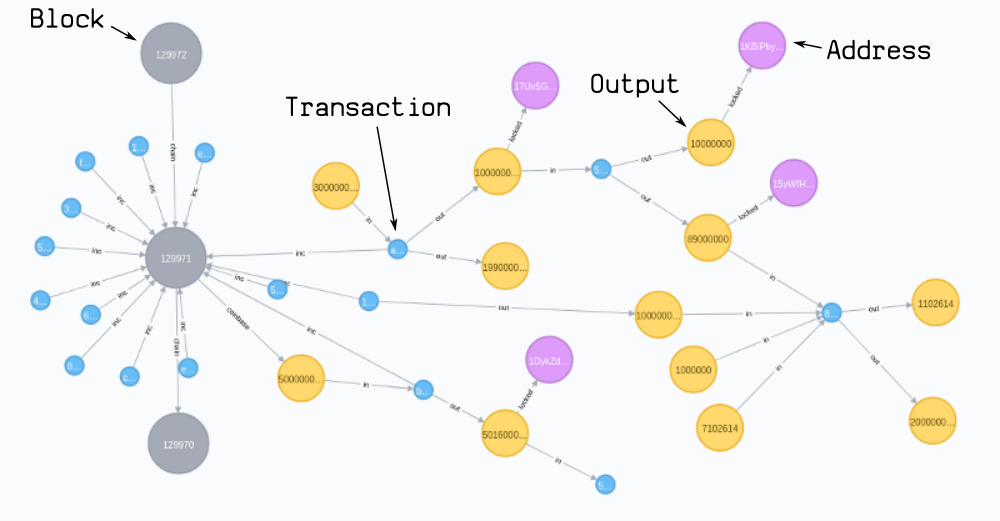
This guide runs through the basic steps for importing the bitcoin blockchain in to a tigergraph graph database.
The whole process is just about taking data from one format (blockchain data), and converting it in to another format (a graph database). The only thing that makes this slightly trickier than typical data conversion is that it's helpful to understand of the structure of bitcoin data before you get started.
however, once you have imported the blockchain in to tigergraph, you can perform analysis on the graph database that would not be possible with SQL databases. For example, you can follow the path of bitcoins to see if two different addresses are connected:
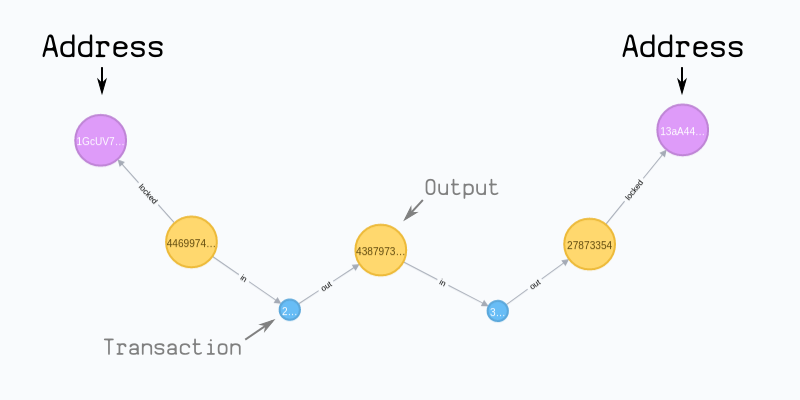
In this guide I will cover:
- How bitcoin works, and what the blockchain is.
- What blockchain data looks like.
- How to import the blockchain data in to tigergraph.
1. What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a computer program.
It's a bit like uTorrent; you run the program, it connects to other computers running the same program, and it shares a file. However, the cool thing about Bitcoin is that anyone can add data to this shared file, and any data already written to the file cannot be tampered with.
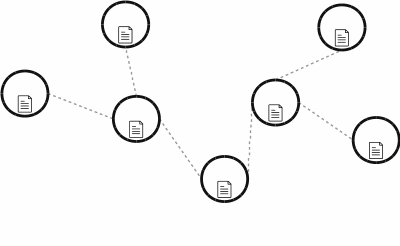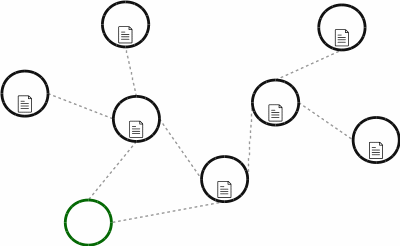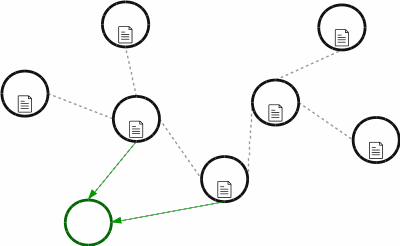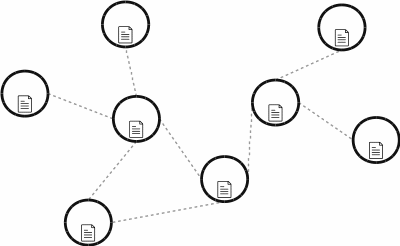
As a result, Bitcoin creates a secure file that is shared on a distributed network.
What can you do with this?
Well, in Bitcoin, each piece of data that gets added to this file is a transaction. Therefore, this decentralised file is being used as a "ledger" for a digital currency.
This ledger is called the blockchain.
2. What does the bitcoin look like?
The blk.dat files contain serialized data of blocks and transactions.
Blocks are separated by magic bytes, which is then followed by the size of the upcoming block.
Each block then begins with a block header:
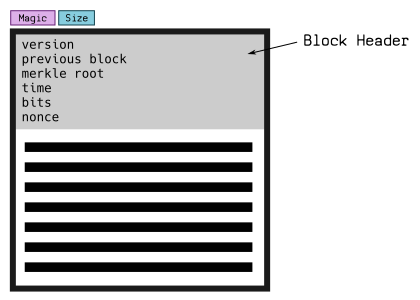
Block Header Example:
{
"version": 00000020,
"previousblock": "6c77f112319ae21489b66774e8acd379044d4a23ea7498000000000000000000",
"merkleroot": "821fe1890186779b2cc232d5dbecfb9119fd46f8a9cfd1141649ff1cd9073744",
"time": 87d8ae59,
"bits": "e93c0118",
"nonce": 32ec0399,
}
Transactions
After the block header, there is a byte that tells you the upcoming number of transactions in the block. After that, you get serialized transaction data, one after the other.
A transaction is just another piece of code again, but they are more structurally interesting.
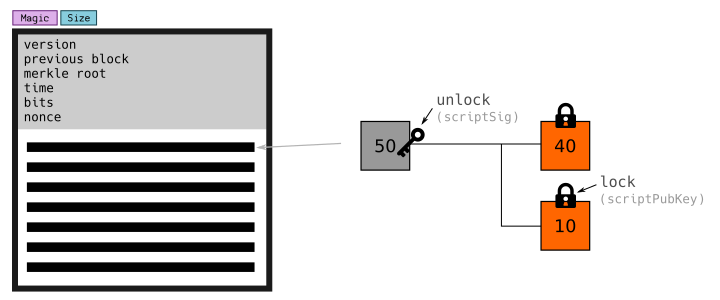
Each transaction has the same pattern:
- Select Outputs (we call these Inputs).
- Unlock these inputs so that they can be spent.
- Create Outputs
- Lock these outputs to a new address.
So after a series of transactions, you have a transaction structure that looks like something this:
Transaction Example:
{
"version": "02000000",
"inputcount": "01",
"inputs": [
{
"txid": "f2f7ee9dda0ba82031858d30d50d3205eea07246c874a0488532014d3b653f03",
"vout": "00000000",
"scriptsigsize": "6a",
"scriptsig": "47304402204df1839028a05b5b303f5c85a66affb7f6010897d317ac9e88dba113bb5a0fe9022053830b50204af15c85c9af2b446338d049672ecfdeb32d5124e0c3c2256248b7012102c06aec784f797fb400001c60aede8e110b1bbd9f8503f0626ef3a7e0ffbec93b",
"sequence": "feffffff"
}
],
"outputcount": "02",
"outputs": [
{
"amount": "00e1f50500000000",
"scriptpubkeysize": "19",
"scriptpubkey": "76a9144120275dbeaeb40920fc71cd8e849c563de1610988ac"
},
{
"amount": "9f16641800000000",
"scriptpubkeysize": "19",
"scriptpubkey": "76a91493fa3301df8b0a268c7d2c3cc4668ea86fddf81588ac"
}
],
"locktime": "61610700"
}
3. How to import bitcoin in to tigergraph.
Well, now we know what the blockchain data represents (and that it looks a lot like a graph), we can go ahead and import it in to tigergraph. We do this by:
- Reading through the blk.dat files.
- Decoding each block and transaction we run in to.
- Converting the decoded block/transaction in to a Cypher query.
Here's a visual guide to how I represent Blocks, Transactions, and Addresses in the database:
Blocks
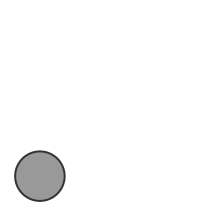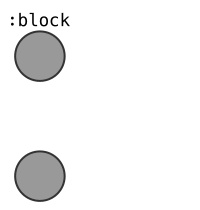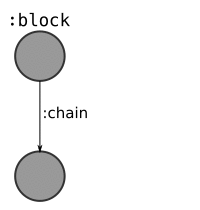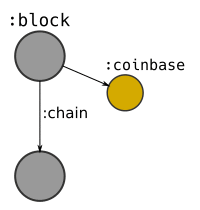
- CREATE a
:blocknode, and connect it to the previous block it builds upon.- SET each field from the block header as properties on this node.
- CREATE a
:coinbasenode coming off each block, as this represents the "new" bitcoins being made available by the block.- SET a value property on this node, which is equal to the block reward for this block.
Transactions
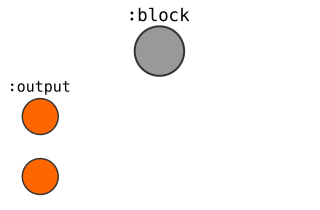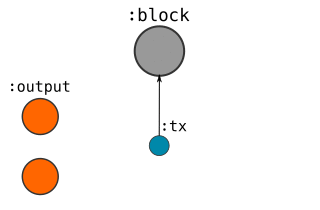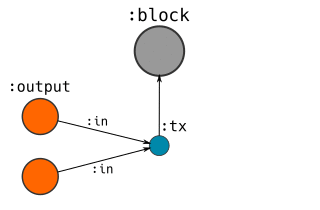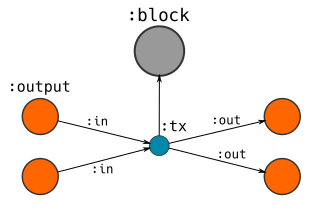
- CREATE a
:txnode, and connect it to the:blockwe had just created.- SET properties (version, locktime) on this node.
- MERGE existing
:outputnodes and relate them[:in]to the:tx.- SET the unlocking code as a property on the relationship.
- CREATE new
:outputnodes that this transaction creates.- SET the respective values and locking codes on these nodes.
Addresses
If the locking code on an :output contains an address...
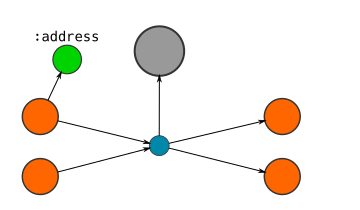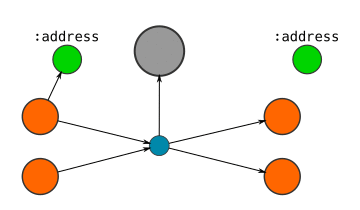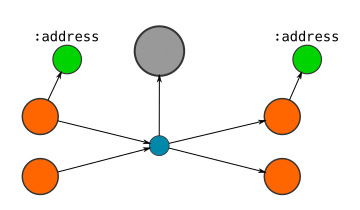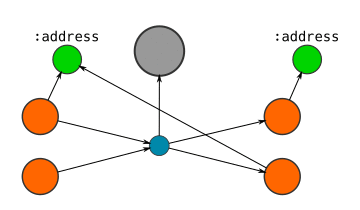
- CREATE an
:addressnode, and connect the output node to it.- SET the address as a property on this node.
- Note: If different outputs are connected to the same address, then they will be connected to the same address node.
4. GSQL Queries
Here are some example cypher queries you could use for the basis of inserting blocks and transactions in to tigergraph.
NOTE: You will need to decode the block headers and transaction data to get the parameters for the cypher queries.
Block
CREATE VERTEX Block (
PRIMARY_ID hash STRING,
number UINT,
version UINT,
timestamp DATETIME,
nonce STRING,
bits STRING,
merkle_root STRING,
size UINT,
stripped_size UINT,
weight UINT,
transaction_count UINT
)
Parameters (example):
{
"blockhash": "00000000000003e690288380c9b27443b86e5a5ff0f8ed2473efbfdacb3014f3",
"version": 536870912,
"prevblock": "000000000000050bc5c1283dceaff83c44d3853c44e004198c59ce153947cbf4",
"merkleroot": "64027d8945666017abaf9c1b7dc61c46df63926584bed7efd6ed11a6889b0bac",
"timestamp": 1500514748,
"bits": "1a0707c7",
"nonce": 2919911776,
"size": 748959,
"txcount": 1926,
}
Transaction
CREATE VERTEX Transaction (
PRIMARY_ID hash STRING,
version UINT,
lock_time UINT,
size UINT,
virtual_size UINT,
input_count UINT,
output_count UINT,
input_value DOUBLE,
output_value DOUBLE,
fee DOUBLE,
is_coinbase BOOL
)
Note: This query uses the FOREACH hack, which acts as a conditional and will only create the :address nodes if the $addresses parameter actually contains an address (i.e. is not empty).
Parameters (example):
{
"txid": "2e2c43d9ef2a07f22e77ed30265cc8c3d669b93b7cab7fe462e84c9f40c7fc5c",
"hash": "00000000000003e690288380c9b27443b86e5a5ff0f8ed2473efbfdacb3014f3",
"i": 1,
"tx": {
"version": 1,
"locktime": 0,
"size": 237,
"weight": 840,
"segwit": "0001"
},
"inputs": [
{
"vin": 0,
"index": "0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000:4294967295",
"scriptSig": "03779c110004bc097059043fa863360c59306259db5b0100000000000a636b706f6f6c212f6d696e65642062792077656564636f646572206d6f6c69206b656b636f696e2f",
"sequence": 4294967295,
"witness": "01200000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"vout": 0,
"index": "2e2c43d9ef2a07f22e77ed30265cc8c3d669b93b7cab7fe462e84c9f40c7fc5c:0",
"value": 166396426,
"scriptPubKey": "76a91427f60a3b92e8a92149b18210457cc6bdc14057be88ac",
"addresses": "14eJ6e2GC4MnQjgutGbJeyGQF195P8GHXY"
},
{
"vout": 1,
"index": "2e2c43d9ef2a07f22e77ed30265cc8c3d669b93b7cab7fe462e84c9f40c7fc5c:1",
"value": 0,
"scriptPubKey": "6a24aa21a9ed98c67ed590e849bccba142a0f1bf5832bc5c094e197827b02211291e135a0c0e",
"addresses": ""
}
]
}
5. Results
If you have inserted the blocks and transactions using the cypher queries above, then these are some examples the kind of results you can get out of the graph database.
Block
INTERPRET QUERY () FOR GRAPH BitcoinGraph {
// Parameter declaration
STRING blockHash = "$blockhash";
// Query logic
start = {Block.*};
target = SELECT t
FROM start:b - (block_txn:txn_block) - Transaction:t
WHERE b.hash == blockHash
ACCUM
PRINT b AS Block, t AS Transaction;
}
Transaction
INTERPRET QUERY () FOR GRAPH BitcoinGraph {
// Parameter
STRING txHash = "$txid";
// Start from all Transaction vertices
start = {Transaction.*};
results = SELECT inp, tx, out, blk, inpAddr, outAddr
FROM start:tx
-(txn_output:txn_output)- :out
-(output_address:output_address)- :outAddr
, :inp - (input_txn:input_txn) -> tx
, inp - (output_address:output_address) -> inpAddr
, tx - (txn_block:txn_block) -> :blk
WHERE tx.hash == txHash
ACCUM
PRINT inp AS Inputs,
tx AS Transaction,
out AS Outputs,
blk AS Block,
inpAddr AS InputAddresses,
outAddr AS OutputAddresses;
}
Address
INTERPRET QUERY () FOR GRAPH BitcoinGraph {
// Parameter
STRING targetAddress = "$address";
// Start from matching Address vertex
start = {Address.*};
results = SELECT o, a
FROM start:a - (address_output:address_output) -> Output:o
WHERE a.address == targetAddress
ACCUM
PRINT a AS Address, o AS Output;
}
Paths
Finding paths between transactions and addresses is probably the most interesting thing you can do with a graph database of the bitcoin blockchain, so here are some examples of cypher queries for that:
Between Outputs
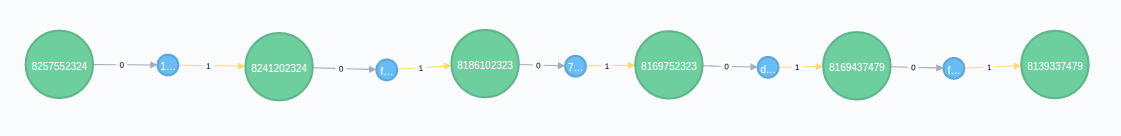
INTERPRET QUERY () FOR GRAPH BitcoinGraph {
// Parameters
STRING startIndex = "$txid:vout";
STRING endIndex = "$txid:out";
// Start from the Output vertices
start = {Output.*};
source = SELECT s FROM start:s WHERE s.transaction_hash_index == startIndex;
target = SELECT e FROM start:e WHERE e.transaction_hash_index == endIndex;
# Perform shortest path search between the two Output vertices
PATHSHORTEST p1 = SELECT shortest_path(source, target, 5)
FROM Output:o
- ((input_txn | output_txn | txn_output | txn_input)) -
Output:o2;
PRINT p1;
}
Between Addresses
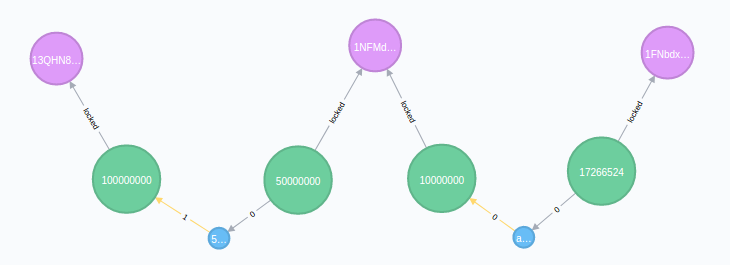
INTERPRET QUERY () FOR GRAPH BitcoinGraph {
// Parameters
STRING startAddr = "$address1";
STRING endAddr = "$address2";
// Match start and end address nodes
startV = {Address.*};
src = SELECT s FROM startV:s WHERE s.address == startAddr;
dst = SELECT d FROM startV:d WHERE d.address == endAddr;
// Find shortest path across Address, Output, Transaction using all edge types
PATHSHORTEST p1 = SELECT shortest_path(src, dst, 6)
FROM Address:a
-(address_output | output_address |
txn_output | output_txn |
input_txn | txn_input)-
ANY;
PRINT p1;
}
6. Conclusion
This has been a simple guide on how you can take the blocks and transactions from blk.dat files (the blockchain) and import them in to a tigergraph database.
I think it's worth the effort if you're looking to do serious analysis on the blockchain. A graph database is a natural fit for bitcoin data, whereas using an SQL database for bitcoin transactions feels like trying to shove a square peg in to a round hole.
I've tried to keep this guide compact, so I haven't covered things like:
- Reading through the blockchain. Reading the blk.dat files is easy enough. However, the annoying thing about these files is that the blocks are not written to these files in sequential order, which makes setting the height on a block or calculating the fee for a transaction a bit trickier (but you can code around it).
- Decoding blocks and transactions. If you want to use the cypher queries above, you will need to get the parameters you require by decoding the block headers and raw transaction data as you go. You could write your own decoders, or you could try using an existing bitcoin library.
- Segregated Witness. I've only given a cypher query for an "original" style transaction, which was the only transaction structure used up until block 481,824. However, the structure of a segwit transaction is only slightly different (but it might need its own cypher query).
Nonetheless, hopefully this guide has been somewhat helpful.
But as always, if you understand how the data works, converting it to a different format is just a matter of sitting down and writing the tool.
Good luck.